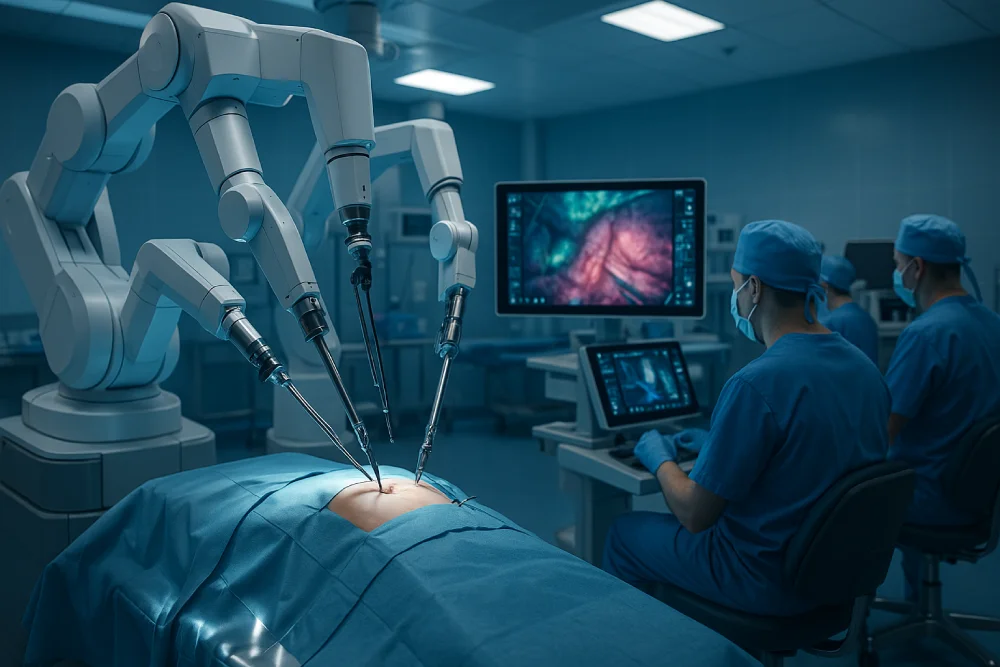
Robotic surgery innovations deliver enhanced precision through tremor elimination and 360-degree instrument rotation, enabling complex procedures previously impossible with traditional methods. Patients experience significantly faster recovery with 20% shorter hospital stays and reduced complications. The technology achieves superior outcomes, including 96% urinary continence rates in prostate surgery and decreased readmission rates from 32% to 21%. Surgeons benefit from reduced fatigue and improved ergonomics. These advances create substantial healthcare cost savings while improving patient satisfaction and long-term functional preservation across multiple medical specialties.
While traditional surgical techniques rely on the inherent limitations of human dexterity, robotic surgical systems have revolutionized operative precision by providing surgeons with capabilities that exceed natural hand movements. These advanced systems deliver instrument control with tremor elimination and 360-degree rotation, enabling delicate maneuvers in confined anatomical spaces while minimizing tissue damage and blood loss.
The integration of high-definition, three-dimensional visualization creates improved visualization quality that surpasses conventional laparoscopic approaches. This enhanced imaging provides better anatomical awareness, allowing surgeons to identify critical structures with unparalleled clarity and depth perception. The combination of superior instrument control and advanced visualization capabilities enables precise dissection, accurate suturing, and safe navigation around vital tissues, ultimately reducing surgical complications and improving patient outcomes across a wide range of surgical specialties.
Robotic surgery applications span multiple medical specialties including urology, gynecology, general surgery, and cardiac surgery, demonstrating the versatility of these systems in enhancing surgical precision across diverse procedural requirements.
Beyond the immediate operative advantages, robotic surgery delivers substantial improvements in post-surgical recovery that fundamentally alter the patient experience. Patients undergoing robotic procedures experience a shorter hospital stay, typically reduced by approximately 20% compared to open surgery—for instance, eight days versus ten days in bladder cancer cases. This faster physical recovery stems from minimally invasive techniques that preserve tissue integrity and reduce trauma.
Recovery protocols are significantly shortened, with catheter use dropping from three weeks to seven days in prostate surgery. Patients report substantially less postoperative pain and require fewer prescription medications. Blood loss decreases dramatically, reducing fatigue and accelerating healing. Additionally, robotic surgery significantly reduces the readmission rate by 52% within 90 days post-operation compared to traditional open procedures. Quality of life scores improve markedly at four-month follow-ups, with enhanced physical function and mobility restoration supporting earlier return to daily activities.
Robotic surgery demonstrates measurable improvements in clinical outcomes across specific procedures, with enhanced precision capabilities translating to reduced complication rates. The superior visualization and instrument dexterity offered by robotic platforms enable surgeons to perform more precise dissections and reconstructions, minimizing inadvertent tissue damage and intraoperative bleeding. These technological advantages contribute to better functional outcomes in select procedures while maintaining stable complication profiles as adoption rates continue to expand across surgical specialties. However, systematic analysis of 154 reviews encompassing 336 studies reveals that limited evidence supports the widespread expansion of robotic surgery beyond certain specialized procedures.
As surgical technology continues to evolve, the clinical evidence increasingly demonstrates that robotic-assisted procedures deliver superior patient outcomes through dramatically reduced complication rates across multiple medical specialties. Studies reveal that robotic surgery shows markedly lower incidences of severe postoperative complications, with rates as low as 1.3% compared to 7.1% in conventional laparoscopic approaches for gastric cancer cases. The improved hand eye coordination provided by robotic systems enables surgeons to perform precise movements that minimize reduced tissue trauma during procedures. This enhanced precision translates to fewer infections, bleeding episodes, and organ injuries across surgical disciplines. Additionally, robotic surgery demonstrates significantly lower conversion rates to open procedures, with some studies showing 0% conversion compared to 2.9% for traditional laparoscopic methods, further reducing patient risk. Patients who undergo robotic abdominoperineal resections benefit from a reduced complication rate along with shorter hospital stays compared to laparoscopic procedures.
While reduced complication rates represent a significant advancement in surgical care, the precision benefits of robotic systems extend far beyond basic safety improvements to deliver measurably superior clinical outcomes across varied medical specialties. Immersive visualization through high-definition 3D imaging enables surgeons to identify critical anatomical structures with unparalleled clarity. Motion stabilization eliminates hand tremor, allowing microscopic precision during delicate procedures. Seven degrees of freedom in instrument movement surpass traditional laparoscopic limitations, facilitating complex maneuvers in confined spaces.
| Precision Feature | Traditional Surgery | Robotic Surgery |
| Hand Tremor Control | Natural tremor present | Complete elimination |
| Instrument Movement | Limited articulation | 7 degrees of freedom |
| Visualization Quality | 2D standard definition | 3D high-definition |
| Motion Scaling | 1:1 movement ratio | Adjustable micro-movements |
These technological advances translate directly into improved surgical margins and enhanced patient outcomes.
Beyond enhanced precision capabilities, robotic surgical systems deliver quantifiable improvements in patient recovery trajectories that fundamentally reshape postoperative care expectations. Hospital stays decrease by approximately 20%, while readmission rates drop from 32% to 21% within 90 days compared to traditional approaches. Surgical complications reduce dramatically, with spinal procedures showing decreases from 12.2% to 6.1% when AI-assisted robotics are employed.
Patient satisfaction reaches 85% positive feedback, reflecting superior recovery experiences. Emotional well being improves in 50% of patients, with 80% reporting easier transitions back to daily activities. Lower postoperative pain scores facilitate quicker mobilization and earlier work resumption. Cancer patients benefit from reduced local-regional recurrence rates, dropping from 4% to 1.6% in three-year follow-ups, demonstrating superior oncological outcomes.
Robotic surgery’s minimally invasive approach fundamentally alters the patient experience through significantly smaller incisions that reduce tissue trauma compared to traditional open procedures. These refined techniques enable patients to recover more quickly with less postoperative pain, decreased scarring, and lower infection risks. The combination of reduced surgical trauma and enhanced precision allows for shorter hospital stays and faster return to normal activities.
As surgical technology advances toward greater precision, minimally invasive robotic procedures have fundamentally altered patient outcomes through dramatically reduced tissue trauma. These systems enable surgeons to perform complex operations through incisions measuring mere centimeters rather than traditional large openings, resulting in substantially less scarring and accelerated healing times.
Robotic instruments provide unparalleled control, allowing implementation of nerve sparing techniques and sophisticated tissue conservation strategies that preserve healthy structures while targeting specific areas. The enhanced 3D visualization and magnified views enable surgeons to maneuver delicate anatomical regions with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues.
Patients experience significantly reduced blood loss, lower infection rates, and decreased post-operative pain. The combination of smaller incisions and precise tissue handling translates into faster recovery periods and improved cosmetic outcomes.
The reduced tissue trauma achieved through robotic surgery directly translates into accelerated patient recovery timelines that consistently outperform traditional surgical approaches. Enhanced surgical visualization enables surgeons to perform precise tissue handling, minimizing blood loss and promoting faster healing. These minimally invasive capabilities significantly reduce hospital stays, with robotic pancreatic and hernia patients discharged approximately three days earlier than those undergoing traditional procedures.
Robotic prostatectomy demonstrates particularly impressive results, reducing hospital stays from three days to overnight visits while decreasing catheter dependency from three weeks to seven days. Gastrointestinal recovery shows marked improvement in colorectal surgeries, with patients achieving first flatus significantly earlier than laparoscopic methods. The combination of reduced procedure duration, decreased infection risks, and minimal tissue disruption creates optimal conditions for rapid functional recovery and earlier return to daily activities.
Several key advances in robotic surgery technology have fundamentally transfigured how surgeons carry out intricate procedures, providing quantifiable enhancements in both exactitude and stamina. Robotic platforms enable surgeons to achieve superior precision through advanced instrument control, with studies demonstrating reduced hand movement from 1.7 cm to 0.6 cm when using systems like Da Vinci. This enhanced dexterity translates into fewer surgical errors and improved patient outcomes.
Ergonomic console designs significantly reduce physical strain during lengthy procedures. Surgeons experience less neck, back, and shoulder fatigue while maintaining seated positions with optimized controls. This reduced mental strain enables enhanced cognitive focus throughout complex operations. Objective performance indicators derived from robotic data provide standardized skill assessment, promoting consistent surgical excellence and accelerated learning curves for medical professionals.
Four revolutionary AI-driven technologies are altering surgical precision by providing surgeons with unparalleled real-time guidance capabilities during robotic procedures. AI-enhanced anatomical visualization creates fluid digital twins that adjust instantly as patient positioning changes, enabling personalized surgical planning while reducing radiation exposure. Computer vision systems analyze video streams to identify critical structures like blood vessels and nerves, highlighting anatomical landmarks to prevent inadvertent damage. Decision support algorithms accelerate intraoperative pathology analysis and predict risks through early warning systems that detect potential bleeding. Workflow optimization tools recognize surgical steps in real-time, predicting case duration and bottlenecks. Despite data integration challenges, these technologies enable real time surgical monitoring that reduces cognitive load, enhances accuracy, and improves patient outcomes through sophisticated predictive analytics and automated guidance systems.
Robotic surgery systems demonstrate significant potential for reducing healthcare costs through decreased hospital resource utilization and lower long-term care expenses. These technologies consistently show shorter hospital stays, reduced ICU time, and fewer complications across multiple surgical procedures, directly translating to decreased immediate hospitalization costs. The economic benefits extend beyond initial treatment periods, with substantially lower readmission rates and reduced follow-up care requirements generating sustained cost savings for healthcare systems.
While initial capital investments in robotic surgical systems may appear substantial, the technology demonstrates significant potential for reducing hospital resource utilization and generating long-term economic benefits through multiple operational efficiencies. Robotic surgeries contribute to effective hospital capacity management by significantly shortening patient stays, freeing beds for additional patients without infrastructure expansion. This reduction decreases hospitalization costs while minimizing hospital-acquired infection risks.
The minimally invasive nature reduces postoperative complications, eliminating needs for additional interventions and readmissions. Enhanced precision decreases blood loss, limiting transfusion requirements and ICU resources. Multi-specialty platform utilization enables efficient resource allocation across departments, maximizing equipment return on investment. Cross-specialty scheduling flexibility increases case throughput while spreading fixed costs over more procedures, ultimately improving operational sustainability and patient flow management.
Beyond immediate operational efficiencies, robotic surgery generates substantial long-term healthcare cost reductions that extend far beyond the hospital setting. Studies estimate the U.S. could save $1.5 to $6.5 billion annually through widespread robotic surgery adoption by avoiding complications and costly follow-ups. The UK’s National Health Service projected savings exceeding £286 million over 20 years from robotic prostatectomy alone due to shorter stays and fewer secondary treatments.
These procedures achieve statistically significant quality-adjusted life years gains while maintaining incremental cost-effectiveness ratios below the $50,000 threshold. Patients experience reduced patient costs through lower out-of-pocket expenses for hospital stays, medications, and complications. Additionally, faster recovery times result in decreased caregiver burden, minimizing indirect economic impacts such as lost productivity and extended rehabilitation requirements throughout patients’ lifetimes.
How do surgical instruments achieve movements that surpass the natural limitations of human hands? Robotic surgical systems accomplish this through sophisticated mechanical engineering that replicates and enhances human dexterity. These instruments filter out natural hand tremors while carrying out steady, precise movements for cutting, suturing, and dissecting. Smaller, thinner robotic arms with multiple joints provide enhanced anatomical access to confined spaces where traditional instruments cannot operate effectively.
| Capability | Advantage |
| Multi-joint articulation | Broader motion ranges than human hands |
| Tremor filtration | Eliminates natural hand shakiness |
| Interchangeable tools | Adaptation during single procedures |
| Extended reach | Long shafts access profound anatomical structures |
| Intuitive controls | Remote operation with enhanced precision |
Adaptable platform designs integrate over 150 innovations, enabling complex minimally invasive procedures previously impossible with conventional surgical approaches.
The sophisticated mechanical precision that enables robotic surgical instruments to surpass human dexterity translates directly into measurably safer patient outcomes. Studies demonstrate significantly lower surgical site infection rates, with robotic procedures showing 1.5% versus 2.9% in traditional surgery for comparable operations. This improvement stems from reduced tissue trauma and minimized contamination risks through smaller incisions that limit internal tissue exposure to external contaminants.
Optimized sanitization protocols specifically designed for robotic equipment further enhance safety profiles. The enhanced three-dimensional visualization and superior control mechanisms decrease accidental tissue damage while reducing inflammatory responses that typically lead to complications. Consequently, patients experience shorter hospital stays—averaging one day compared to two days for conventional approaches—facilitating faster recovery and reducing exposure to hospital-acquired infections.
What distinguishes robotic surgery’s impact extends far beyond immediate procedural benefits to encompass significant improvements in patients’ long-term functional outcomes and overall quality of life. Organ preservation techniques enabled by robotic precision demonstrate exceptional success rates, with 96% of prostate surgery patients achieving complete urinary continence within one year and 97% maintaining satisfactory sexual function after bilateral nerve-sparing procedures.
Long term outcomes research consistently validates these functional advantages, showing five-year biochemical recurrence-free survival rates of 77% while maintaining 100% cancer-specific survival. The minimally invasive nature reduces major complications and accelerates recovery, with patients experiencing shorter hospital stays and improved quality of life metrics. This technological advancement successfully balances oncological effectiveness with preserved functionality.
At Dr. Brian Harkins, we believe robotic surgery innovations are a revolutionary advancement in modern healthcare, delivering measurable benefits across multiple dimensions of patient care. Our systems provide enhanced precision, enable minimally invasive approaches, and support superior clinical outcomes — all of which contribute to improved patient experiences and reduced overall healthcare costs. As we continue to advance these technologies, Dr. Brian Harkins is committed to setting new standards for surgical excellence while preserving long-term functionality and enhancing quality of life for patients worldwide.
Unlike traditional open surgery, which requires large surgery with incisions, robot-assisted surgery and minimally invasive surgery use smaller access points, reducing trauma and recovery time. This shift in the operating room is supported by robotic surgery platforms like the da Vinci system, which enhance visualization, dexterity, and precision.
While laparoscopic surgery already provides many benefits of minimally invasive surgery, robotic surgery offers surgeons superior range of motion, better ergonomics, and enhanced control. Studies have found that robotic procedures deliver less pain, faster recovery, and a lower risk of infection compared with laparoscopic techniques.
Surgeons use robotic systems by sitting at a console where they use the robotic instruments to control a surgical robot with enhanced precision. This approach improves outcomes in spine surgery, mitral valve surgery, and robotic thoracic surgery, proving the versatility of robotic surgical procedures.
The benefits to patients include shorter recovery, less pain, reduced scarring, and fewer complications. Robotic surgery allows surgeons to perform delicate operations that surgery might not otherwise permit with conventional methods, creating better functional outcomes across specialties.
When comparing robotic versus open or laparoscopic approaches, robotic surgery can reduce blood loss, minimize hospital stays, and lower complication risks. The increase in robotic adoption is driven by these consistent improvements in safety and quality across the health system.
Robotic surgeons benefit from real-time oversight in robotic surgery through enhanced visualization, tremor filtration, and magnified 3D imaging. A surgery team in the operating room supports the lead surgeon, ensuring redundancy and safety throughout the procedure.
The acceptance of robotic surgery has expanded significantly, with an academic medical center study showing surgery often transitions from open surgery to laparoscopic and robotic approaches as patients learn more information about robotic surgery and its positive outcomes.
Robotic surgery involves state-of-the-art medical devices like the da Vinci robotic platform, which gives access to robotic precision for complex cases. These robotic systems can help surgeons reach confined areas, making it possible to perform minimally invasive and robotic interventions that previously required open procedures.
Transitioning to robotic surgery has allowed hospitals to make robotic surgery more available to a wider range of patients. As robotic surgery becomes mainstream, robotic technology is being applied to complex fields like spine surgery and oncology, showing how robotic surgery allows broader patient access across the medical center.
Patient recovery after surgery depends on the method. Robotic surgery may offer faster healing, lower complication rates, and improved precision. Versus robotic approaches, traditional open surgery requires longer hospitalization. In short, surgery include better safety profiles and improved long-term outcomes when using robotic surgery.

Dr. Brian Harkins is a renowned surgeon specializing in advanced, minimally invasive, and robotic surgical techniques. With a dedication to innovation and personalized patient care, he has transformed countless lives by delivering exceptional outcomes.
I want a website like this, where do i start?